Does Electrical Stimulation Help Healing?
Jun 15th 2025
Electrical stimulation has evolved far beyond its early use for basic pain relief. Today, it's an integral part of many physical therapy and rehabilitation programs, used to accelerate healing, restore muscle function, and support recovery in both acute and chronic conditions.
Whether applied after surgery, during stroke rehabilitation, or in the treatment of long-standing wounds, this non-invasive therapy works by harnessing controlled electrical currents to stimulate the body's natural repair mechanisms.
As research and clinical use expand, electrical stimulation is becoming a trusted tool for enhancing recovery outcomes across a wide range of medical settings.
In this blog, we explore how it works, when it's most effective, and how high-quality therapeutic devices, like those developed by Pantheon Research, play a key role in delivering safe and effective results.
What Is Electrical Stimulation in Therapy?
Electrical stimulation, often referred to as E-stim, is a therapeutic technique that uses low-voltage electrical currents to stimulate nerves or muscles. It's commonly used by physical therapists and rehabilitation professionals to manage pain, improve mobility, and support recovery from injury, all without invasive procedures or medications.
Electrical stimulation is widely respected for being both non-invasive and clinically supported. Research shows it plays a meaningful role in both acute and chronic care settings, especially for managing musculoskeletal and neurological conditions such as spinal cord injury, stroke, and chronic pain
How Does Electrical Stimulation Support Healing?
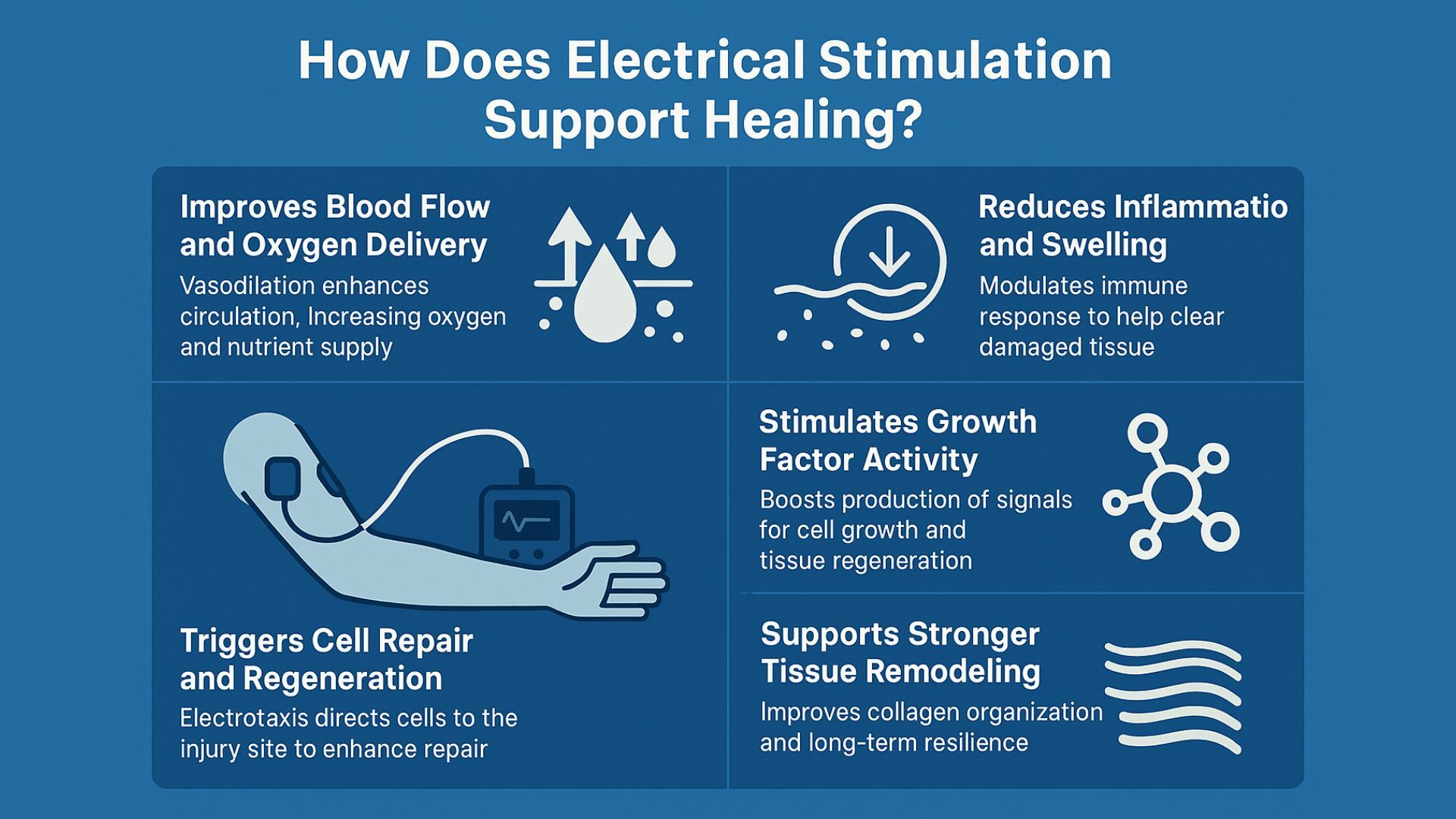
Electrical stimulation supports healing by boosting the body’s repair systems - not just easing pain, but actively helping damaged tissue regenerate, inflammation resolve faster, and circulation improve.
1. Improves Blood Flow and Oxygen Delivery
When electrical pulses are applied to the skin, they can trigger vasodilation, a widening of blood vessels, which improves local circulation. This increased blood flow delivers more oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, both essential for repair and healing.
Multiple studies have shown that electrical stimulation, including TENS and EMS, significantly increases blood flow within minutes of application, helping the body remove waste products and accelerate the healing process
2. Reduces Inflammation and Swelling
Inflammation is a necessary part of healing, but too much of it can stall recovery. Electrical stimulation helps modulate the inflammatory response, guiding immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils to the site of injury to clean up damaged tissue efficiently.
This process supports a smooth transition into the next healing phase - tissue formation and lowers the risk of chronic swelling or delayed recovery.
3. Triggers Cell Repair and Regeneration
Electrical stimulation mimics the body’s natural bioelectric signals, encouraging cells to migrate to the injury site, a process called electrotaxis. This helps:
- Keratinocytes rebuild the skin
- Fibroblasts produce collagen for tissue strength
- Endothelial cells form new blood vessels (angiogenesis)
Together, this accelerates wound closure and ensures the new tissue is well-supplied with blood and nutrients.
4. Stimulates Growth Factor Activity
E-stim enhances the production of natural growth signals like VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and EGF (epidermal growth factor). These proteins speed up cell growth, division, and tissue regeneration, especially in chronic wounds or after surgery.
5. Supports Stronger Tissue Remodeling
In the final stage of healing, electrical stimulation helps rebuild tissue with stronger, better-organized collagen, especially important in scar formation or muscle injuries. It promotes the transition from weaker type-III collagen to durable type-I collagen, improving long-term tissue resilience.
When Is Electrical Stimulation Most Effective?
Electrical stimulation is most effective when used as a supportive therapy, especially in situations where the body’s natural healing or muscle activation is slow or impaired. While it’s not a cure-all, it’s proven to speed up recovery, reduce pain, and enhance muscle function across various clinical scenarios.
1. Chronic and Slow-Healing Wounds
Electrical stimulation is highly effective for wounds that aren't healing well on their own, like diabetic foot ulcers, pressure sores, or venous leg ulcers. In these cases, low-intensity currents can improve blood flow, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue regrowth.
One study reported that 65% of diabetic foot ulcers healed with ES versus 35% with sham treatment over 12 weeks
2. Post-Surgical Recovery
After surgery, such as ACL repairs or knee replacements, electrical stimulation helps activate surrounding muscles that may have weakened due to immobilization. Using NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation), patients often regain strength quicker and prevent early muscle wasting.
This makes ES a valuable part of early rehab protocols in orthopedic recovery.
In post-surgical rehab or during neuro-muscular re-education, using evidence-based tools like the 8c.Pro helps deliver targeted electrical stimulation with programmable settings, enabling practitioners to support muscle recovery and nerve retraining more effectively.
3. Managing Chronic Pain
E-stim, especially TENS, is frequently used for chronic pain conditions like:
- Fibromyalgia
- Arthritis
- Neuropathy
- Chronic low back pain
It helps by blocking pain signals and triggering endorphins, providing relief that can last for hours after treatment. While it doesn’t fix the underlying condition, it often allows patients to stay active and reduce medication reliance.
4. Rebuilding Muscle Strength After Injury or Stroke
For people recovering from strokes or spinal cord injuries, Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) can help re-train muscle movement. It’s also useful in sports rehab or after long periods of immobilization (like a cast), helping restore strength and prevent atrophy.
E-stim may also be used to reduce spasms, improve range of motion, or support neuromuscular re-education.
5. As a Complement to Physical Therapy
Electrical stimulation works best when combined with other rehab tools, like stretching, strengthening, and manual therapy. It reduces pain, making it easier to do the exercises that rebuild function, while also speeding up circulation and healing.
Who Should Consider Using Electrical Stimulation?
Electrical stimulation is not just for athletes or people recovering from surgery - it’s a versatile tool that supports recovery, pain relief, and wound healing across a wide range of situations. Still, it's most effective when used under the guidance of a medical professional.
Ideal Candidates for E-Stim Therapy
Athletes in Recovery
Whether recovering from a muscle strain or aiming to speed up post-workout recovery, athletes often use EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) to:
- Prevent muscle atrophy
- Improve blood flow
- Manage inflammation
EMS is commonly integrated into rehab routines to maintain muscle tone during periods of reduced activity or immobilization
People with Chronic or Post-Surgical Pain
TENS or IFC stimulation can help relieve pain from conditions like:
This is especially useful for individuals looking to reduce their dependence on pain medications.
Elderly Individuals with Poor Circulation
As circulation tends to decline with age, some older adults may benefit from electrical stimulation’s ability to:
- Enhance peripheral blood flow
- Improve oxygenation in tissues
- Accelerate the healing of minor skin injuries or ulcers
Stroke or Neurological Rehab Patients
People recovering from strokes, spinal cord injuries, or neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis or cerebral palsy may use Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) to:
- Re-train paralyzed or weak muscles
- Improve motor function (e.g., walking, grasping)
- Support nerve and muscle re-education
When Electrical Stimulation May Not Be Suitable
While generally safe, electrical stimulation is not recommended or should be used cautiously in the following cases:
- Individuals with implanted medical devices (e.g., pacemakers)
- Pregnancy (especially over the abdomen or pelvic area)
- Cancer in the treatment zone
- Severe cardiac conditions or uncontrolled arrhythmias
- Active DVT or recent blood clots
- Over open wounds (unless directed for wound therapy)
- Children under age 3, unless supervised by a specialist
- Areas with poor sensation, where discomfort can’t be reported
- People with epilepsy, especially over the head or neck
Always consult a healthcare provider before beginning electrical stimulation, especially if you fall into any of the above groups.
What Are the Different Types of Electrical Stimulation Used in Healing?
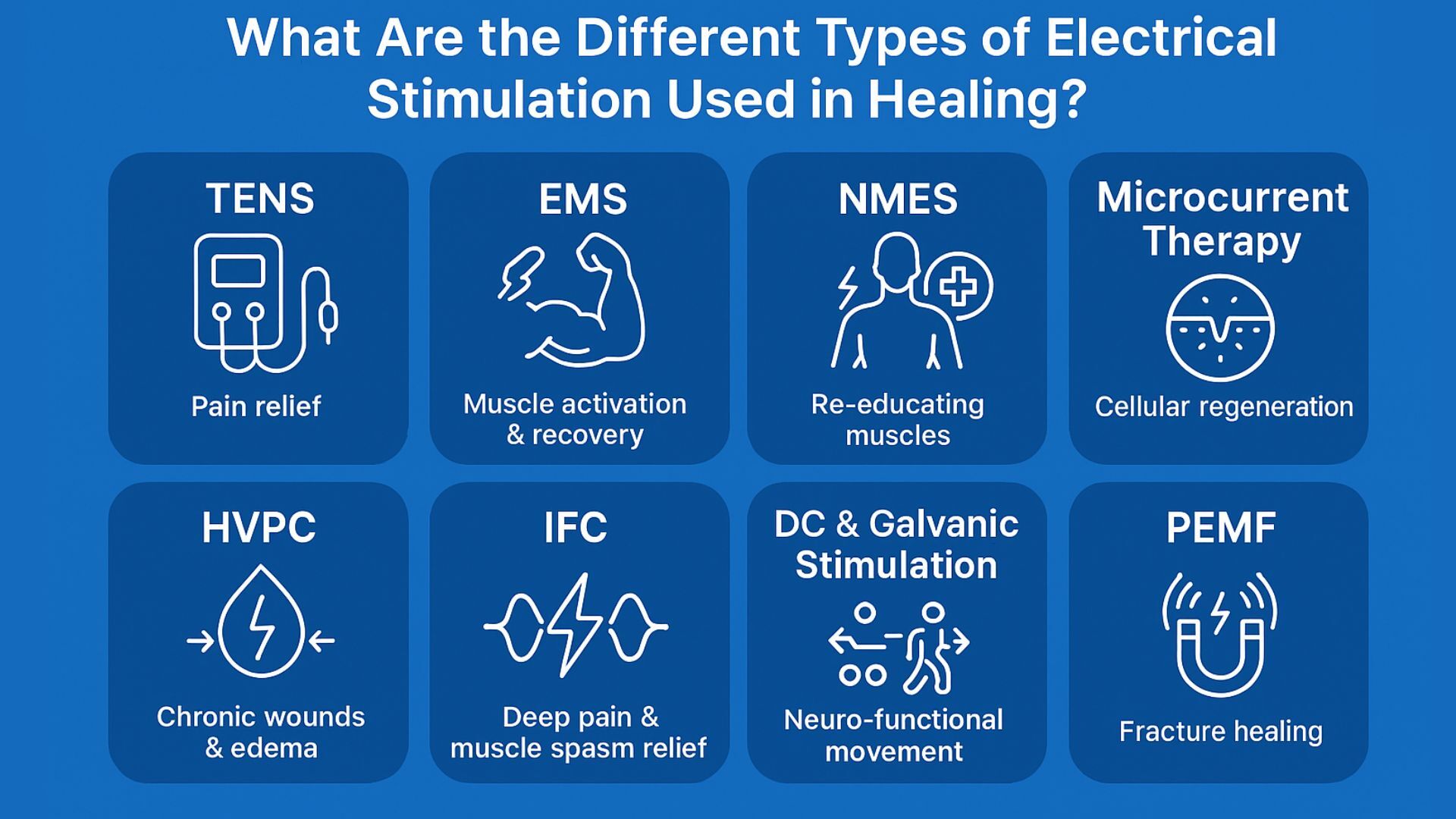
Different types of electrical stimulation (E-stim) serve different purposes - from reducing pain and improving muscle function to enhancing wound healing and tissue regeneration. Each type uses a specific waveform or frequency pattern to achieve a targeted outcome.
For professionals needing flexible control over frequency, pulse width, and waveform modulation, devices like the 12c.Pro Advanced offers enhanced electroacupuncture functionality, making them ideal for both clinical precision and advanced therapy customization.
Let’s break them down by function, purpose, and device relevance:
1. TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
Best for: Pain relief, TENS sends low-voltage pulses through the skin to stimulate sensory nerves, blocking pain signals from reaching the brain. It’s widely used for conditions like:
- Fibromyalgia
- Arthritis
- Post-surgical pain
By reducing pain, it also helps patients stay active during recovery.
2. EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation)
Best for: Muscle activation & recovery, EMS stimulates motor nerves to cause muscle contractions. It’s popular in sports and rehab for:
- Preventing muscle loss during immobility
- Enhancing recovery post-injury
- Supporting muscle endurance
The Electrostimulator 4c.Pro offers EMS capabilities with adjustable parameters for both clinical and home use.
3. NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation)
Best for: Re-educating weakened muscles, NMES works like EMS but focuses on restoring function to muscles impaired by:
- Stroke
- Neurological injuries
- Surgical procedures
It’s often integrated into neuro-rehab routines to restore movement and prevent atrophy. Devices like the Clinical Microcurrent Stimulator support NMES functionality in therapeutic settings.
4. Microcurrent Therapy
Best for: Cellular regeneration and wound healing, Microcurrent uses sub-sensory currents (less than 1mA) to mimic the body’s natural bioelectrical activity. It's especially effective for:
- Hard-to-heal wounds
- Skin repair
- Scar tissue softening
A clinical study published in Advances in Wound Care shows microcurrent therapy increases ATP production, the energy fuel for cells, by up to 500%, boosting healing at the cellular level.
5. HVPC (High-Voltage Pulsed Current)
Best for: Chronic wounds and edema, HVPC is used primarily in wound care to:
- Improve blood circulation
- Reduce swelling
- Stimulate tissue regeneration
It's particularly useful for diabetic ulcers and pressure injuries. Studies suggest HVPC accelerates wound closure and reduces infection risk when used with standard care.
6. IFC (Interferential Current)
Best for: Deep pain and muscle spasm relief, IFC uses intersecting medium-frequency currents that penetrate deeper than TENS. It helps:
- Relieve lower back pain
- Ease joint inflammation
- Reduce post-injury swelling
Its comfort level is often preferred in cases where deeper tissue pain must be managed non-invasively.
7. FES (Functional Electrical Stimulation)
Best for: Neuro-functional movement training. FES activates muscles during functional tasks like walking or grasping. It’s ideal for:
- Stroke survivors
- Spinal cord injury patients
- Children with cerebral palsy
Mimicking natural muscle activation patterns, it helps realistically retrain lost movement.
8. DC (Direct Current) & Galvanic Stimulation
Best for: Directed cell migration and tissue growth
DC stimulation influences charged cell movement (a process called galvanotaxis) toward wound sites. It can:
- Promote fibroblast and keratinocyte migration
- Help heal ischemic wounds
- Support re-epithelialization
9. PEMF (Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy)
While not a direct electrical current, PEMF creates microcurrents in tissues using magnetic fields. It's shown promise in:
- Healing fractures
- Enhancing soft tissue regeneration
- Managing chronic pain
PEMF is often used in conjunction with traditional electrotherapy.
The effectiveness of therapy often depends on choosing the right Electroacupuncture Devices that offer adjustable frequency, pulse control, and safety features - all essential for precise stimulation in both traditional and modern clinical setups.
Conclusion
Electrical stimulation isn’t just a temporary fix - it’s a clinically backed method to support the body’s healing systems. Whether you're recovering from surgery, managing chronic pain, healing difficult wounds, or working through neurological rehab, the right type of stimulation can make recovery faster, safer, and more effective.
But success depends on the quality and suitability of the device you use. That’s where Pantheon Research stands out.
As a trusted leader in advanced electrotherapy solutions, Pantheon offers some of the Best electro-acupuncture stimulators on the market - built for precision, durability, and clinical performance. Their devices are trusted by professionals around the world and come with a 6-Year Replacement Warranty, giving users long-term confidence and protection in case of defects or issues.
And for those looking to build clinical skills or deepen their understanding, Pantheon also provides access to Microcurrent Therapy Training - a comprehensive program that bridges science with practical application.
